chalazion: symptoms, prevention and treatment - Dr Yeung Ho Hong 楊浩康
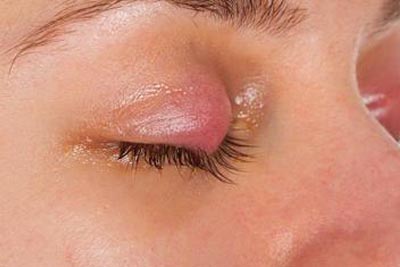
What are the symptoms of eyelid cysts?
Chalazion is a common eye condition characterized by a small, firm lump on the eyelid. Typically painless, it may grow over time, affecting the eyelid’s appearance or causing mild irritation. It results from a blocked oil gland on the eyelid, preventing normal secretion drainage. Though usually benign, untreated cases can lead to infection or other eye complications.
How to Prevent Eyelid Swellings
“The key to preventing eyelid cysts is to maintain eye hygiene and avoid blockage of the oil glands.”
Blocked oil glands causing chalazion may stem from various factors, including chronic blepharitis, local irritation from expired or low-quality cosmetics, or improper contact lens hygiene. Chronic conditions like rosacea or excessive sebum production also raise blockage risks, leading to abnormal oil secretion and eventual gland obstruction.
Clinically, chalazion presents as one or more small, painless eyelid lumps. Larger cysts may cause mild redness or inflammation, potentially leading to slight eyelid drooping, affecting vision or aesthetics. Some patients report a foreign body sensation or discomfort, worsened by windy conditions or prolonged eye strain. If infected, the lump may become painful, red, hot, and purulent, requiring immediate medical attention.
Treatment of Eyelid Cysts
Diagnosing chalazion typically involves a clinical eye exam by an ophthalmologist, assessing the lump’s shape, size, and color, alongside patient history and symptom progression. In complex cases, slit-lamp examination or biopsy may be used to rule out other conditions like eyelid tumors or severe blepharitis.
First-line treatment is conservative, involving warm compresses applied several times daily for 10-15 minutes. This improves blood flow, softens clogged oil, and aids natural drainage. For mild cases, gentle eyelid massage may help dislodge blockages. To prevent complications, antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be prescribed if infection signs appear, controlling inflammation and infection.
For recurrent or large chalazia affecting vision, surgical removal may be necessary. Post-surgical care is critical to prevent recurrence and minimize scarring.
Preventing chalazion involves good eye hygiene and lifestyle adjustments. Regularly cleaning the face and eye makeup tools, avoiding expired or unsuitable cosmetics, reduces blockage risks. Contact lens wearers must follow strict cleaning, disinfection, and replacement protocols. Adequate eye rest and avoiding overuse help minimize eyelid inflammation, lowering chalazion likelihood.
In summary, though chalazion is a common, mostly benign eye condition, untreated cases can affect appearance and, in severe instances, vision or lead to complications. Early diagnosis and timely treatment—via warm compresses, medication, or surgery—yield good outcomes for most patients. Enhanced daily eye care and healthy habits are key to prevention.
