Epidermoid cyst(粉瘤): symptoms, prevention and treatment - Dr Yeung Ho Hong 楊浩康
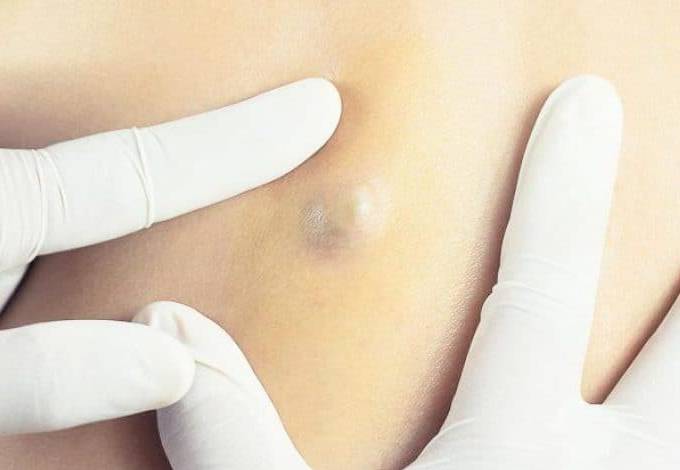
What are the symptoms of epidermoid cyst
A sebaceous cyst, formally known as an epidermoid cyst, is a common and benign skin tumor. It is primarily formed by the abnormal growth of epidermal cells that mistakenly enter the dermis layer, creating a sac-like structure within the skin. This condition can occur on the face, neck, back, or even around the genital area, typically presenting as one or more round nodules. Since sebaceous cysts are often painless and smooth in appearance during their early stages, most patients discover them incidentally during routine physical examinations or cosmetic care.
The formation of a sebaceous cyst is closely related to clogged hair follicles. When normal sebum and keratin cannot be effectively expelled from the follicle, these secretions accumulate deep within the skin. Combined with the local tissue’s response to injury or inflammation, this leads to the proliferation and accumulation of epidermal cells in the dermis, forming a cyst. At the center of the cyst, a small black opening, often referred to as a “blackhead,” is commonly visible. This serves as a channel for the discharge of keratin material from within the cyst. In some cases, external pressure may cause a cheesy white or yellow substance to be extruded from the cyst.
Clinically, most sebaceous cysts do not present obvious symptoms or cause discomfort, making them incidental findings. However, if the cyst becomes inflamed due to friction, pressure, or bacterial infection, the surrounding skin may become red, swollen, painful, or even purulent. In such cases, patients may experience localized itching, burning, or mild tenderness. If these infectious changes are not addressed promptly, they can not only affect appearance but also lead to persistent discomfort or localized tissue damage.
The diagnosis of a sebaceous cyst largely relies on a doctor’s clinical experience, with a preliminary judgment often made through visual inspection and medical history review. In cases where clinical presentation is atypical or malignancy needs to be ruled out, a biopsy or cytological examination may be performed. Pathological examination typically reveals that the cyst wall is composed of keratinized epidermal cells, with the cyst filled with keratin, sebum, and other cellular debris, aiding in the final diagnosis.
In terms of treatment, for asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic sebaceous cysts, doctors often recommend regular observation without immediate intervention. However, if the cyst becomes infected, red, swollen, painful, or affects appearance, further treatment is required. Initial management may involve oral or topical antibiotics to control infection and inflammation, while warm compresses and gentle massage can help promote the discharge of cyst contents. For recurrent or significantly enlarged cysts, surgical excision is often the definitive treatment. Surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia and allows for complete cyst removal, though it may leave a small scar, which should be clearly communicated to the patient beforehand.
It should be noted that even after surgical excision, some patients may still experience cyst recurrence, which is related to the extent of the surgical removal and any residual epidermal cells. Therefore, postoperative care and follow-up are crucial. Patients should keep the incision site clean, avoid repeated friction, and follow the physician’s instructions for proper localized care to reduce the risk of recurrence. Regular follow-up visits help in the timely detection and management of potential new cyst formation.
On the prevention front, while there is no specific method to completely eliminate the occurrence of sebaceous cysts, maintaining good skin hygiene, avoiding unnecessary skin trauma, and using skincare products correctly can help reduce the incidence of this condition. This is especially important for individuals with excessive sebum production or a tendency toward follicular obstruction, who should pay extra attention to skin cleansing and regular care. Additionally, promptly addressing minor skin injuries is a key measure in preventing the development of sebaceous cysts.
In summary, a sebaceous cyst is a common and typically benign skin tumor associated with clogged hair follicles and abnormal epidermal cell proliferation. While most sebaceous cysts do not cause significant discomfort, active treatment is necessary if infection or rapid growth occurs. From clinical diagnosis to treatment options, physicians tailor individualized plans based on the patient’s specific condition. Proper postoperative care and regular follow-up can effectively reduce the risk of recurrence. With scientific management and good skincare habits, patients can achieve favorable treatment outcomes and an improved quality of life.
