How to Treat Rosacea(玫瑰痤瘡)? - Dr Yeung Ho Hong 楊浩康
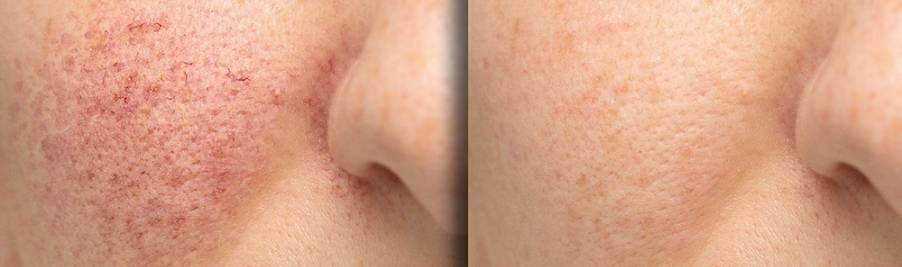
Rosacea Symptoms and Causes
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the facial skin. It manifests in various forms, with patients potentially experiencing facial redness, papules, pustules, visible blood vessels, and symptoms such as dry or stinging skin. Depending on its type and severity, doctors will adopt personalized treatment plans, including topical creams, oral medications, and other specialized therapies, aimed at reducing symptoms and preventing recurrence.
Commonly used treatments: drugs and lasers
Topical creams are the cornerstone of rosacea treatment and are suitable for mild to moderate cases. Medications such as metronidazole ('甲硝唑') and azelaic acid ('壬二酸') can effectively suppress skin inflammation, reducing redness and the occurrence of papules. Meanwhile, brimonidine ('溴莫尼定') is a newer topical drug primarily targeting facial redness. It works by constricting blood vessels to reduce the visibility of erythema, offering significant and rapid results.
For patients with more severe papules or pustules, doctors may recommend oral antibiotics. For instance, doxycycline ('多西環素'), minocycline ('米諾環素'), and metronidazole ('甲硝唑') are commonly used as oral treatments for rosacea. Oral antibiotics provide both antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects, helping to effectively alleviate inflammatory lesions. Additionally, long-term low-dose antibiotic use can reduce the recurrence rate of rosacea and improve the overall condition of the skin.
Beyond medication, vascular laser therapy is another option for rosacea patients. Laser treatment primarily targets the improvement of facial telangiectasia (visible small blood vessels) and chronic erythema. It works by using high-energy light beams to shrink abnormally dilated blood vessels, thereby reducing redness. The effects of laser therapy typically require multiple sessions to stabilize and are suitable for patients with severe erythema or those who respond poorly to medication.
Advice for daily care and prevention
Daily skincare is crucial for managing rosacea. Patients should avoid triggers such as spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeinated beverages, as these irritants may worsen facial redness and inflammation. Additionally, maintaining good sun protection habits is essential to minimize UV damage to the skin. When going outdoors, using sunscreen, wearing wide-brimmed hats, or carrying umbrellas can help reduce symptom exacerbation caused by sun exposure.
When choosing skincare and cosmetic products, patients should opt for hypoallergenic options with minimal additives, avoiding products containing fragrances or alcohol, which may irritate the skin and further aggravate the condition. Furthermore, keeping the skin clean and moderately moisturized can reduce irritation and help improve the skin’s barrier function.
Rosacea is a skin condition that requires long-term management, and patients should actively collaborate with dermatologists to develop and follow personalized treatment plans. Based on the patient’s specific condition, doctors may combine topical creams, oral medications, and physical therapies, offering tailored advice to reduce the likelihood of recurrence. Regular follow-ups allow doctors to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment plans in a timely manner, ensuring more effective control of the condition.
It’s worth noting that psychological factors and stress may influence the course of rosacea. Patients should strive to maintain a positive mood and reduce stress sources. Appropriate exercise, a healthy diet, and a regular routine can all contribute to overall well-being and indirectly aid in improving skin condition.
In summary, treating rosacea requires comprehensive management from multiple angles. Combining medication with daily care is key to achieving optimal results. Patients need to remain consistent, actively follow their doctor’s advice, and maintain healthy lifestyle habits to effectively control the condition and enhance their quality of life.
