What are the side effects of Isotretinoin? - Dr Yeung Ho Hong 楊浩康
Common Side Effects of Isotretinoin
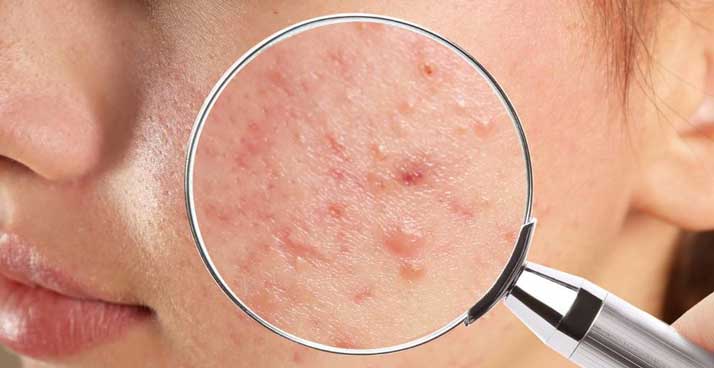
Oral Isotretinoin, commonly known as A-acid, is an important medication for treating severe acne, and its efficacy has been widely recognized. However, before starting treatment, patients must fully understand the various potential side effects this drug may cause. It’s worth noting that these side effects do not necessarily occur in every user, but high-risk groups—such as pregnant women, women planning to conceive, patients with abnormal liver function, those with excessive vitamin A levels, or individuals with elevated blood lipid levels—should exercise extra caution when considering its use.
Before starting Isotretinoin (異維A酸), doctors typically arrange detailed blood tests, including liver function and lipid level assessments, to ensure the patient can safely take the medication. In the early stages of treatment, some acne patients may experience a so-called "flare-up period," a temporary worsening of acne. However, as treatment continues and drug levels stabilize, this condition usually improves gradually, and most patients eventually see significant skin improvement.
One of the most common groups of side effects associated with oral Isotretinoin relates to dryness of the skin and mucous membranes. During treatment, patients may experience nasal mucosal dryness, cheilitis (lip inflammation), dry dermatitis, and dry eye syndrome, which can cause some disruption to daily life. To alleviate these discomforts, doctors often recommend moisturizing care, along with the use of lip balm and artificial tears to relieve symptoms.
Effects of Isotretinoin on Liver Function and Blood Lipid Profile
Long-term use of Isotretinoin may also affect liver function and blood lipid levels. Some patients may notice elevated liver enzymes or abnormal lipid values, such as triglycerides, during treatment. Therefore, regular blood tests are necessary throughout the treatment period. If abnormalities are detected, doctors may adjust the dosage or pause treatment to prevent further liver damage or serious complications like pancreatitis.
Prevention, control and attention to isotretinoin
Additionally, another significant risk of oral Isotretinoin is its potential harm to a fetus. The drug has strong teratogenic effects, meaning women taking it must strictly avoid pregnancy before, during, and after treatment. Typically, contraception is required starting one month before treatment, continuing throughout the course, and for at least one month after discontinuation. For breastfeeding mothers, use of this medication is also discouraged to ensure infant safety.
In extremely rare cases, oral Isotretinoin may cause benign intracranial hypertension (pseudo-tumor cerebri), manifesting as headaches, blurred vision, or other neurological symptoms. If patients experience such symptoms, they should seek medical attention immediately. Furthermore, combining Isotretinoin with tetracycline-class drugs may increase the risk of side effects, so concurrent use of these medications should be avoided.
Other less common but noteworthy side effects include temporary hair loss, headaches, joint pain, muscle pain, visual disturbances, and mood swings. These side effects are typically more noticeable during or at the beginning of treatment but often subside as the patient’s body adjusts to the medication. Nevertheless, for individuals with sensitive constitutions or pre-existing conditions, regular monitoring is crucial to allow timely adjustments to the treatment plan.
In summary, Isotretinoin is highly effective in treating severe acne, but it also carries a range of potential side effects. To minimize risks, patients must undergo thorough clinical evaluation and necessary blood tests before use, strictly follow medical advice during treatment, and adopt comprehensive care measures. Only by doing so can the drug achieve its optimal therapeutic effect while safeguarding the patient’s health, truly fulfilling the goal of "curing the disease with the right medicine."
